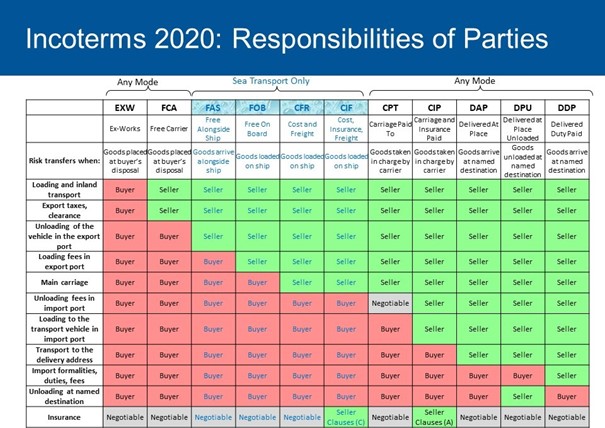
Incoterms 2020 Rules
EXW (EX WORKS) Delivery
It is the delivery method that puts the seller at least risk. In the form of EXW delivery, it is sufficient for the exporter to have the goods ready in packaging at the place where the goods to be exported will be loaded (factory, warehouse, etc.). Here, the importer assumes all responsibility. Through its own agency, it sends the transport vehicle to pick up the goods in the exporter's country, loads the goods, passes it through customs, brings it to its own country (if an intermediate carrier is used, loads it to the main carrier) and sends it to the place where the goods will be unloaded by passing it through the customs in its own country. Customs, transportation, dispatch, loading, unloading and their costs in both countries belong to the importer.
FCA (FREE CARRIER) Delivery
In the form of Free CarrierFCA delivery, the seller loads the goods from his own place to the intermediate carrier and carries out customs clearance, delivers them to the carrier at the designated place with whichever main carrier will go, and the seller's responsibility ends here. If the loading is at the seller's location, the responsibility lies with the seller, and elsewhere it is the buyer's.
FOB (FREE ON BOARD) Delivery
In the form of FOB delivery, the seller applies the same FAS delivery procedure and loads the goods unloaded at the port over the ship and transfers the responsibility to the buyer.
CFR (COST AND FREIGHT) Delivery
CFR or C&F is used only in sea transportation. The exporter loads the goods on the transport vehicle, carries out the customs clearance, puts the goods in the port, loads them on the ship and pays all expenses and freight until they are unloaded at the designated port of destination. Although the transportation belongs to the seller, all risks (loss, damage, etc.) during transportation belong to the buyer. In other words, the seller only bears the freight cost. Shipping and customs clearance in the buyer's country are the buyer's responsibility.
CIF (COST, INSURANCE, FREIGHT) Delivery
In the form of CIF delivery, the exporter takes out marine insurance in addition to the CFR conditions. Although the transportation cost belongs to the seller, the risks belong to the buyer.
CPT (CARRIAGE PAID TO) Delivery
In the CPT delivery form, the exporter assumes the responsibility to pay the freight up to the pre-agreed destination. It is used in all modes of transport, especially in multi-vehicle transport. From the moment the seller transfers the goods to the custody of the first carrier, all risk related to the goods, excluding freight, passes to the buyer.
CIP (Carriage and Insurance Paid to)
In the form of CIP delivery, the exporter undertakes the transportation insurance in addition to the conditions in the CPT.
DAP (DELIVERED AT PLACE) Delivery
It undertakes the task of DEQ, DAF, DES and DDU delivery forms included and removed in Incoterms 2000. It can be used in all modes of transport. In this form of delivery, after the exporter has loaded the goods and passed them through the customs of his own country – if he has used an intermediate carrier – loads the main carrier and reaches the agreed destination (port, warehouse, logistics terminal, or the importer's warehouse) and leaves the unloading to the buyer. Customs clearance, customs duty and other costs in the importer's country belong to the importer.
DPU (DELIVERED AT PLACE UNLOADED) Delivery
In this form of delivery, which has replaced DAT, the exporter loads the goods and passes them through the customs of their own country – if an intermediate carrier is used – loads them on the main carrier and unloads them at the agreed destination (port, warehouse, logistics terminal, or the importer's warehouse). However, customs clearance, customs duty and other costs in the importer's country belong to the importer.
DDP (DELIVERED DUTY PAID) – Delivery
Unloading is the responsibility of the buyer. Taxes and costs in both customs, freight, intermediate carrier organization and costs belong to the exporter. The responsibility of the importer in EXW passes to the exporter in DDP.